Android Context Analysis
Android Context 分析
继承结构类图:
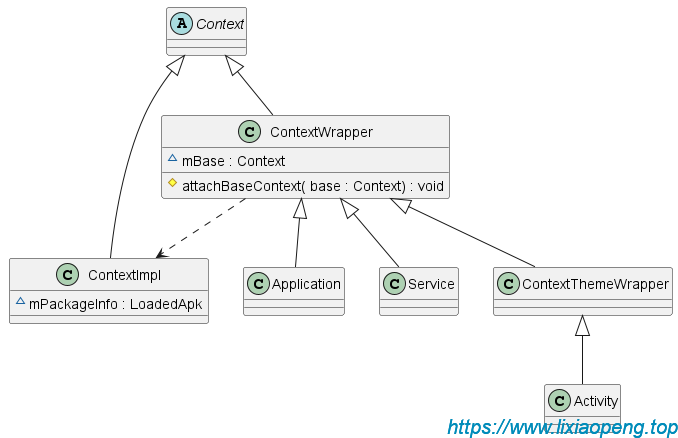
ContextWrapper是上下文的包装类,ContextImpl是上下文的实现类,Activity是ContextThemeWrapper的直接子类。
getApplicationContext都做了什么
翻看ContextWrapper源码:
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
public ContextWrapper(Context base) {
mBase = base;
}
/**
* Set the base context for this ContextWrapper. All calls will then be
* delegated to the base context. Throws
* IllegalStateException if a base context has already been set.
*
* @param base The new base context for this wrapper.
*/
protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) {
if (mBase != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
@Override
public Context getApplicationContext() {
return mBase.getApplicationContext();
}
....
}ContextWrapper的getApplicationContext方法直接调用mBase的getApplicationContext方法,mBase实际上是ContextImpl类实例,通过上面源码看到,在ContextWrapper类的attachBaseContext方法为其赋值。
什么时候调用的Application的attachBaseContext方法?
在ContextWrapper子类Application类的attach方法中:
final void attach(Context context) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mLoadedApk = ContextImpl.getImpl(context).mPackageInfo;
}而Application的attach方法是在Instrumentation类的newApplication方法中调用.
static public Application newApplication(Class<?> clazz, Context context)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
Application app = (Application)clazz.newInstance();
app.attach(context);
return app;
}继续向上追溯,Instrumentation的newApplication方法是在LoadApk的makeApplication方法中调用:
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
...
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
...
return app;
}最终调用LoadApk的makeApplication方法的地方都在ActivityThread的多个方法中:performLaunchActivity,handleReceiver,handleCreateService,handleBindApplication,attach.
Related Link
本文为Adamin90原创文章,转载无需和我联系,但请注明来自http://www.lixiaopeng.top

请先登录后发表评论
- 最新评论
- 总共0条评论




